Diabetes
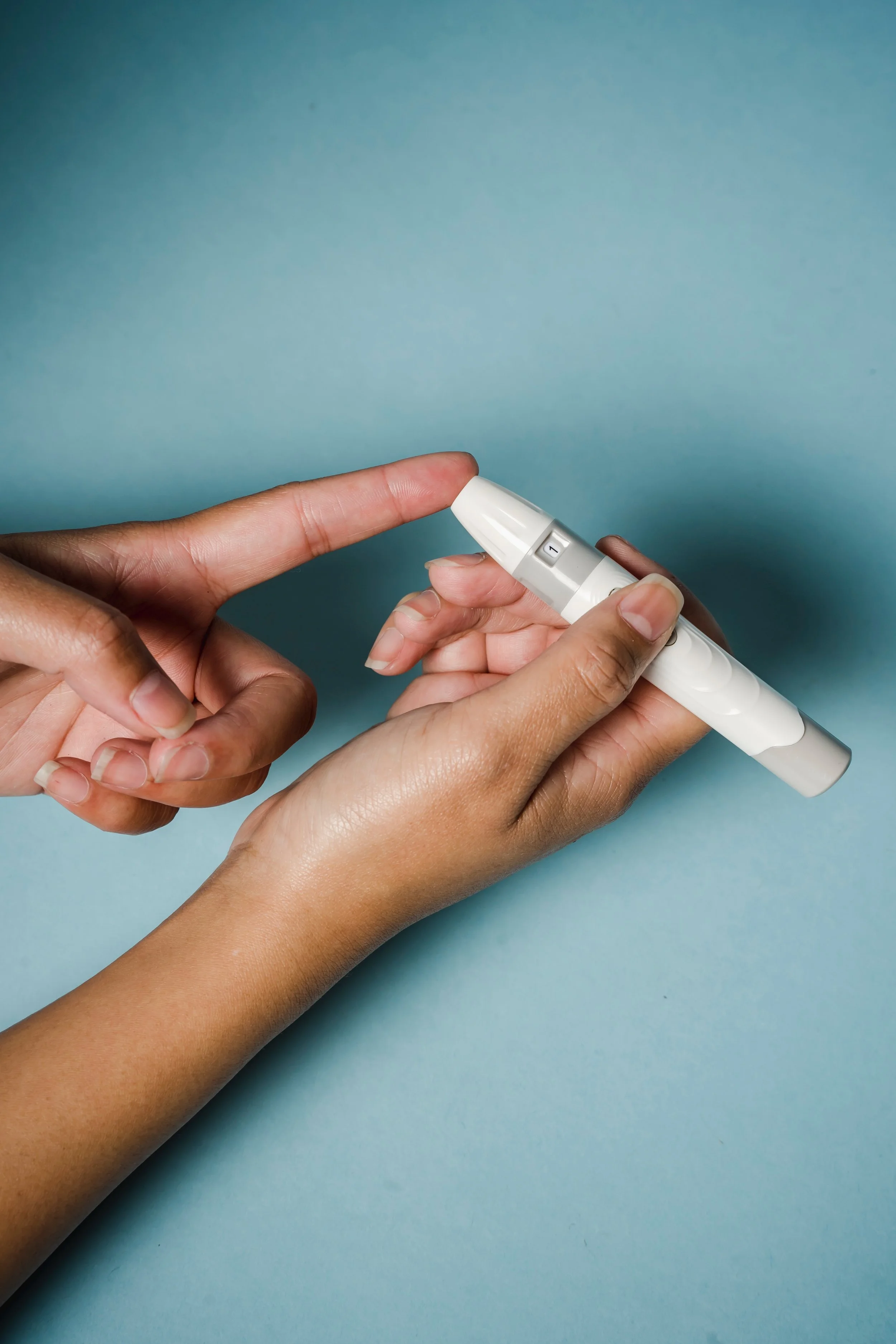
Learning about diabetes is the first step to improving your health
Pre-Diabetes
Prediabetes is a serious health condition where your blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough yet to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. According to the CDC, more than 1 in 3 U.S. adults have prediabetes—that’s 88 million people—but the majority of people don’t know they have it.
The good news is that by making small healthy lifestyle changes, it is possible to prevent type 2 diabetes and even reverse your prediabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes is a disease that occurs when your blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high. Over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause health problems, such as heart disease, nerve damage, eye problems, and kidney disease. You can take steps to manage and even reverse Type 2 Diabetes.
An estimated 30.3 million people in the United States, or 9.4 percent of the population, have diabetes. About one in four people with diabetes don’t know they have the disease.
According to the US National Library of Medicine, Diabetes is predicted to rise by 54% from 2015 to 2030!
2015 - 35,644,000
2020 - 43,271,000
2025 - 49,799,000
2030 - 54,913,000
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. Diabetes means your blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high. Too much glucose in your blood is not good for you or your baby.
Gestational diabetes is usually diagnosed in the 24th to 28th week of pregnancy. Managing your gestational diabetes can help you and your baby stay healthy. You can protect your own and your baby’s health by taking action right away to manage your blood glucose levels.
High blood glucose levels during pregnancy can cause problems for your baby, such as
being born too early
weighing too much, which can make delivery difficult and injure your baby
having low blood glucose, also called hypoglycemia, right after birth
having breathing problems
Your baby also will be more likely to become overweight and develop type 2 diabetes as he or she gets older.
If you have gestational diabetes, you are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes later in life. Over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause health problems such as diabetic retinopathy, heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage.



